Can force be negative: Yes force can be negative as force is a vector quantity that depends upon magnitude and direction. The negative sign signifies only the direction.
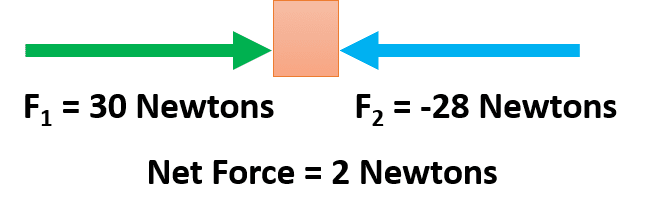
Table of Contents
Negative Force
- If the applied force is in the opposite direction to the displacement of the moving object then the force will be negative.
- Forces that are aimed at the right are usually called positive forces.
- Forces that are aimed to the left are usually said to be in a negative direction.
- In the above figure, F2 is a negative 28 Newtons force, and F1 is a positive 30 newtons force.
.
What is Force?
The push or pull on an object with mass causes it to change its velocity.
It is a vector quantity and its unit is Newton.
Force = mass x acceleration
Force is an external agent capable of changing the state of rest or state of motion of a particular body. It can move or tend to move an object or it can stop or tend to stop an object. It is a vector quantity.
Units of Force
- Newton
- Dyne (1 Newton = 100000 dynes)
- pound-force (1 Newton = 0.224 pound-force)
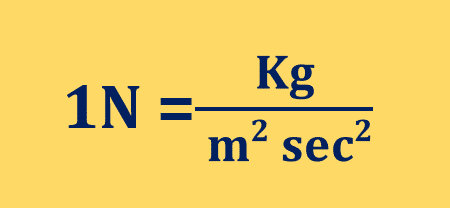
What is 1 Newton?
It is defined as the force necessary to provide a mass of one kilogram with an acceleration of one meter per second per second. One newton is equal to a force of 100,000 dynes in the centimetre-gram-second (CGS) system, or a force of about 0.2248 pounds in the foot-pound-second (English, or customary) system.
units “meter per second squared
1 N =1kg x 1 m/sec2
Key Points
- The unit of force is Newton.
- Force can be negative or positive.
- If the acceleration is negative, the force will negative
- Usually, Force acting toward the right is taken as positive
- The magnitude of the force is always a positive (or zero) quantity.
- Force acting towards the left is taken as negative
- The force applied to an object is directly proportional to the mass and acceleration of an object
- Vector quantity. As described by the magnitude and direction.
- Force per unit area is called pressure.
- LMT-2
- Force formula: F = m a
- Can force be negative? Yes

Examples of Negative Force in Physics
In physics, forces are often described as being either positive or negative, depending on the direction in which they act. Some examples of negative forces include:
- Frictional force: Frictional force acts in the opposite direction to an object’s motion and can slow it down or bring it to a stop.
- Air resistance: When an object is moving through the air, air resistance acts against its motion and can also slow it down.
- Tension force: Tension force acts along the length of a rope or cable and is negative when it pulls in the opposite direction to an object’s motion.
- Gravitational force: When an object is near the surface of a planet or other celestial body, it experiences a gravitational force that pulls it towards the centre of the body. If the object is moving away from the body, the gravitational force acts against its motion and is negative.
Negative Force In simple words
Force is a vector quantity and depends upon the direction in which we apply force.
Consider that we are applying force to an object but we aren’t able to move that object in the direction of the force. In this case, the object is applying a reaction force that is greater than the applied force. Therefore, the net force is negative.
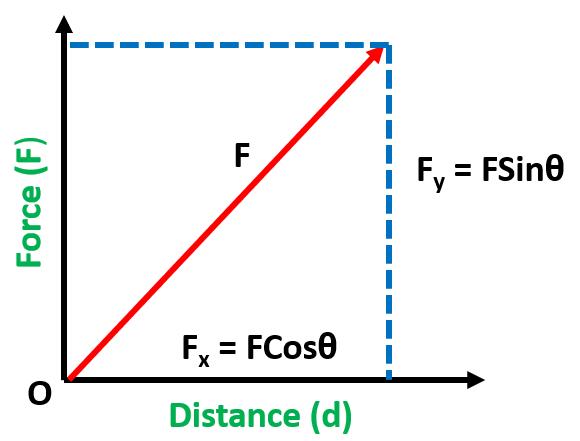
Horizontal and vertical components of force
Consider a force (F) applied to an object. The force F is making an angle θ with the surface on which the body is moved as shown in the figure at left. The applied force F can be resolved into its perpendicular components Fx and Fy.
Fx = Fcosθ ——— (1)
Fy = Fsinθ ——— (2)
When Force and displacement are not parallel then only the x-component of force (Fx) causes the body to move on the surface.
Examples of Force
- If we apply force on a cart either by pushing or pulling it. The push may move the cart or change the direction of its motion or may stop the moving cart.
- We apply force to cut an apple with a knife by pushing its sharp edge into the apple.
- When something is squashed or stretched, it changes shape and pushes or pulls on the thing that is squashing or stretching it
- The force of your foot pushing on the pedal when you ride your bike
- The force of a magnet on a paper clip when the magnet moves the paper clip towards it.
- A person floating in still water
- A wrecking ball hanging vertically from a cable
- Helicopter hovering in place
- A child pushing a wagon on level ground
How does Force work?
- Force can make a body that is at rest to move.
- It can stop a moving body or slow it down.
- Force can accelerate the speed of a moving body.
- It can also change the direction of a moving body along with its shape and size.
Dimension of Force
F =ma, Therefore, 1N = 1kg x 1m/sec2
[F]=[MLT-2]

Different Types of Force
The table below shows different types of force.
| SR.No | Type | Definition |
| 1 | Weight force | The force of gravity acting on an object is due to its mass. An object’s weight is directed down, toward the centre of the gravitating body.. |
| 2 | Normal force | The Normal force (Fn) between two solids in contact prevents them from occupying the same space. It is directed perpendicular to the surface. |
| 3 | Friction force | The frictional force (fr) between solids in contact resists their motion across one another. It is directed opposite the direction of relative motion or the intended direction of motion of either of the surfaces. |
| 4 | Tension force | Tension force (T) is exerted by an object being pulled upon from opposite ends like a string, rope, cable, chain, etc. Tension is directed along the axis of the object. |
| 5 | Elasticity force | Elasticity (E) is a force exerted by an object under deformation (typically tension or compression) to return to its original shape when released. For instance, the movement of the spring or rubber band behaves elastically. |
Quick Links
The inertia of a Body
The inertia of a body is its property due to which it resists any change in the state of rest or uniform motion.
The inertia of a body depends upon its mass of the body. The greater the mass of the body, the greater will be the inertia of the body.
Example problems Force
Example 1: A man pushes a 5.2 kg box with 10N of force. What is the resultant acceleration?
Newton’s second law states that F=ma.
In this problem, F=10 N and m=5.2kg. Therefore, 10N = 5.2kg (a)
acceleration = 10N/5.2kg = 1.92 m/sec2
Example 2: A cyclist of mass 50 kg exerts a force of 200N to move his bicycle with an acceleration of 3 m/sec2. How much is the force of friction between the road and the tires?
In this problem, the mass is 50 kg and the acceleration is 3 m/sec2.
Applied force (Fa) = 200N
Net force (Fn) =m x a = (50 kg)(3 m/sec2) = 150 kg m/sec2 =150N
Since Net force (Fn) = Applied force (Fa) – Force of friction (fr)
Fn = 200N -fr
fr =200N- 150N = 50N
First Law Of Motion
A body continues its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line provided no net force acts on it. According to Newton’s first law of motion, a body at rest provided no net force acts on it. This part of the law is true as we observe that objects do not move by themselves unless someone moves them.
Examples of the First Law of Motion
- A book lying on a table remains at rest as long as no net force acts on it.
- A rolling ball on rough ground stops earlier than that rolled on smooth ground. It is because the rough surface offers great friction. If there were no force to oppose the motion of a body then the moving body would never stop.
Law of Inertia
Since Newton’s first law of motion deals with the initial property of matter Newton’s first law of motion is also known as the law of inertia.
Example of Inertia
- When a bus takes a sharp turn, passengers fall in the outward direction. It is due to inertia that they want to continue their motion in a straight line and thus fall outward.
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
Newton’s second law of motion deals with a situation when a net force acts on a body. It states ” When a net force acts on a body, it produces an acceleration in the body in the direction of the net force. The magnitude of this acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on the body and inversely proportional to its mass”.
Mathematical Form of Newton’s Second Law
If a force produces an acceleration in a body of mass m the
acceleration (a) ∝ Force (F)
acceleration ∝ 1/m
Combing equations 1 and 2
a ∝ F/m Therefore, a =kF/m
Where k is a proportionality constant. In SI units, the value of k is 1.
When m =1kg, F=1N then a =1m/sec.
a = F/m so F =ma
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
To every action, there is always an equal but opposite reaction.
Explanation of Newton’s Third law of motion
Newton’s third law of motion deals with the reaction of a body when a force acts on it. Let body A exerts a force on body B, body B reacts against this force and exerts a force on body A. The force exerted by body B on A is called reaction force.
According to this law, the action is always accompanied by a reaction force and the two forces must always be equal and opposite. Action and reaction forces act on different bodies.
Examples of Newton’s Third Law of Motion
- Take an air-filled balloon as shown in fig. When a balloon is set free, the air inside it rushes out and the balloon moves forward. In this example, the action is by the balloon that pushes the air out of it when set free. The reaction of the air which escapes from the balloon acts on the balloon. It is due to this reaction of escaping air that moves the balloon forward.
- A rocket moves on the same principle. When fuel burns, hot gases escape from its tail at a very high speed. The reaction of these gases on the rocket causes it to move opposite to these rushing out of its tail.
Can Velocity be Negative?
To answer the question “can velocity be negative“, we need to understand vector quantities.
In vectors, the negative sign only represents the direction and nothing else. Positive and negative signs depend upon our choice of coordinate system.
Since velocity is a vector quantity, velocity can be negative depending on its direction.
Related Links
Mechanical Energy| 7 Examples
Light Energy| 5- Easy Examples
Instantaneous Velocity| Easy Key Points
Momentum Equation| Examples
Kinetic Energy
The Spring Constant & Spring Force Concept
Summary
- The answer to the question ” Can force be negative” is simply Yes.
- Force is a vector quantity and depends upon magnitude and direction.
- The negative symbol just identifies the direction.
- The force produces the mass and acceleration of an object.
- When an object is slowing down, its acceleration is negative (direction opposite to the velocity).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the simple definition of force?
A push or pull on an object is referred to as force. It could be caused by gravity, magnetism, or anything else that causes a mass to accelerate.
2. What is the net force?
The vector sum of all the forces acting on an object is the net force. That is, the net force is equal to the sum of all forces, taking into mind that a force is a vector, and two forces of identical size and opposing direction cancel each other out.
3. What are the types of force?
Four fundamental forces in physics are gravitational, electromagnetic, strong, and weak forces. They regulate how things or particles interact and decay.
4. What is strain energy and how it is different from resilence?
Strain energy is elastic, which means that when the stress is removed, the material tends to recover. Resilience is the feature of a material that allows it to hold energy without permanent distortion; the energy is released as soon as the load is removed, and thus the body does not deform permanently.
5. Can displacement be negative?
Displacement can be negative since it is a vector variable that depends on magnitude and direction. The negative sign just indicates the direction. Check the full article “can displacement be negative?”.
6. What is a state function?
A state function is a property that depends on the state of a system and is independent of the path taken to get it. Pressure and temperature, for example, are state functions.
7. What is negative work?
Work can be negative if the applied force is in the opposite direction to the moving object’s displacement. Please refer to the full article “Can work be negative?”.
8. Damped oscillation?
A damped oscillation is one that gradually fades away with time. A swinging pendulum, a weight on a spring, and a resistor-inductor-capacitor (RLC) circuit are all examples.
9. Crest of a wave?
The portion of the transverse waves above the mean level is known as the crest of a wave. The section of transverse waves below the mean level is referred to as the wave’s trough.
Please refer to the full article “Crest of a wave”.
10. What is atmospheric pressure?
Atmospheric pressure is the force imposed on things by the air or the Earth’s atmosphere.
The average value of atmospheric pressure at sea level is specified as 1 atmosphere (atm).
11. Displacement physics?
Displacement in physics is a vector with a length equal to the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of a moving object.
12. What is gravitational potential energy?
Gravitational potential energy (w) is the energy that an item has as a result of its location in a gravitational field. If the item is pushed straight up at a constant speed, the force (F) necessary to hoist it to the height (h) is equal to its weight (mg).
13. Relativistic kinetic energy?
According to the relativistic kinetic energy equation, when an object’s velocity approaches the speed of light, its energy approaches infinity. As a result, exceeding this speed restriction is impossible.
14. Gamma decay?
Gamma decay is the discharge of a gamma (γ) ray photon, a type of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, as a result of the radioactive decay of a nucleus. The energy spectrum is often in the 100 keV to 10 MeV range.
15. Is titanium magnetic?
Titanium is a paramagnetic material that is very faintly attracted to magnets. The fundamental reason of its paramagnetic property is the presence of four unpaired electrons in its electrical structure.
Please refer to the article “Is titanium magnetic?”.
Consider that we are trying to move an object but we aren’t able to move that object in the direction of the force. In this case, the object is applying a reaction force that is greater than the applied force. Therefore, the net force is negative.
Since force is directly proportional to acceleration. so negative acceleration means negative force
Author
Umair Javed
Umair has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
He has a Masters degree in Materials Science.
More Links
Velocity Time Graph
Angular Displacement Formula| Easy Examples
Cubic Foot of Water Weight
The Otto Cycle| A Simple Overview
Mass vs Weight| 5 Easy Examples
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023



