Tensile stress is the stress that causes things to pull apart. It may be described as the quantity of force applied along an elastic rod divided by the cross-sectional area of the rod in a direction perpendicular to the applied force.
In simple words, tensile stress causes the elongation of any material along the axis of the load applied to the material. It is a state in which the load applied to an object tends to pull or stretch the material along the line of application of the force.
This article explains the definition of tensile stress along with the formula and SI unit of tensile stress.
Table of Contents
Definition of Tensile Stress
Tensile stress is defined as the force per unit area exerted on the material in order to pull it apart or stretch it. Tensile strain is an object’s extension per unit of the original length. Many mechanical properties of a material can be determined by a tensile test.
As an example, Consider a thin metal strip being pulled at both ends. Tensile stress is applied to the strip. The metallic strip tears when the tensile force exceeds a particular threshold. The tensile tension at which ripping occurs is the strip’s tensile strength.
Tensile Stress Daily Life Examples
Tensile stress, also known as tension, is a type of mechanical stress that results from pulling or stretching a material. Here are some examples of tensile stress:
- Pulling a rope or a chain: When you pull a rope or a chain, you create tensile stress in the material. The rope or chain will stretch as a result of the force applied.
- Stretching a rubber band: When you stretch a rubber band, you create tensile stress in the material. The rubber band will elongate and eventually return to its original shape when the force is released.
- Tension in a suspension bridge: The cables of a suspension bridge are under constant tensile stress as they support the weight of the roadway and the vehicles and people crossing the bridge.
- Tensile testing: Tensile testing is a common method used in materials science to evaluate the strength of materials under tension. The material is stretched until it fails, and the amount of force required to break the material is measured.
- Tension in a trampoline: When someone jumps on a trampoline, the material of the trampoline is subjected to tensile stress. The trampoline stretches and then returns to its original shape, which allows the jumper to bounce back up.
These are just a few examples of tensile stress. Tensile stress can occur in any material that is subjected to a pulling or stretching force.
Tensile Stress Formula
This tensile stress is defined as the force associated with the stretching per unit area. The symbol σ denotes the tensile stress.
σT = Tensile Force (FT)/cross-section area (A0)
- σT is the tensile stress in pascal (Pa); (1Pa=1N/m2)
- FT is the applied tensile force, in newtons (N);
- A0 is the initial cross-sectional area, in meters (m).

Important Definitions
- Ultimate tensile strength: the maximum stress that a material can withstand when a force is applied to it.
- Elastic modulus: the ratio of stress to tensile strain in the case of perfectly elastic material deformation.
- Fracture stress: the greatest stress experienced by the material’s crack point prior to failure.
- Resilience modulus: This quantity is the ratio of the tensile stress and the double of the material’s Young’s modulus.
- Elastic limit: The maximum stress that may be given to an item without causing permanent (plastic) deformation.
Stress in Physics
The magnitude of the forces that induce deformation is measured by stress. Stress is often defined as force per unit area. Tensile stress occurs when forces draw on an object, causing it to extend, as when stretching an elastic band. Compressive stress arises when forces compress an item. Bulk stress arises when an item, such as a submarine in the depths of the ocean, is pressed from all sides (or volume stress). When two materials brush against or glide over each other, shear stress arises. Please see the full article “Stress in Physics”.
Yield Point
The yield point of material occurs when it transitions from elastic behavior (in which releasing the applied force restores the material to its original shape) to plastic behavior (where deformation is permanent).
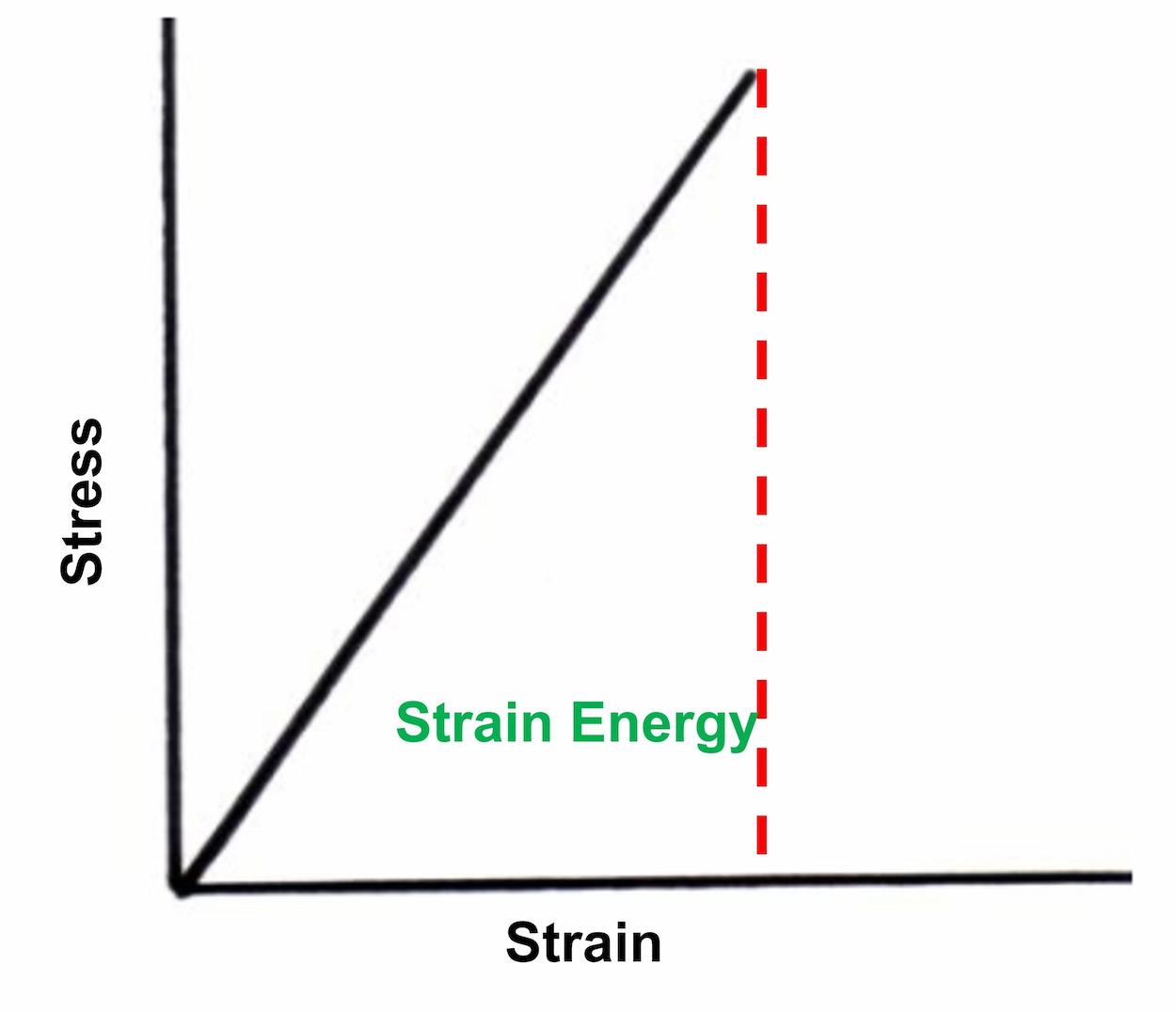
Strain energy
Strain energy is a type of potential energy stored in an item due to elastic deformation. When an item is deformed from its unstressed state, the external work done on it is turned into (and is considered equivalent to) the strain energy contained in it.
Related Links
What Is Malleability in Metal?
Can Force be Negative?| Easy Explanation
Energy-The Ability to do Work
Carbon-Glass Hybrid Composites
Can Work Be Negative?| Easy Explanation & Examples
Carbon Fibre Braided Composite Tubes
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Flexural strength?
A material’s flexural strength is the highest bending stress that can be applied to it before it yields.
2. The spring constant?
The spring constant, k, is a measure of the stiffness of the spring. It depends on the spring and the material. The bigger the spring constant, the stiffer and harder the spring is to extend.
3. What is a metal?
Metals have properties such as malleability, ductility, conductivity, brightness, – and solidity.
Metals are also unique materials found in rock.
4. What is fatigue testing?
Fatigue testing of thermoset composites entails applying cyclic force to a thermoset composite coupon. These tests are used to detect crack growth data, identify critical regions, and demonstrate the safety of fatigue-prone places.
5. What is the difference between Tensile Stress and Compressive Stress?
The main difference between tensile and compressive stress is that tensile tension causes elongation while compressive stress causes shortening. Some materials are strong when subjected to tensile stress yet weak when subjected to compressive stress.
More Links
Mass vs Weight| 5 Easy Examples
Elastic Potential Energy| Definition, Formula, and Examples
Can Momentum be Negative?
The Otto Cycle| A Simple Overview
Surface Energy of a Liquid| Definition, and Examples
Relativistic Kinetic Energy| Easy Explanation
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023