White light is a combination of all colors (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet) in nearly equal proportions. White things seem white because they reflect all visible wavelengths of light that shine on them, making the light appear white to humans. Colored objects, on the other hand, reflect only a portion of the wavelengths; the rest gets absorbed.
Keep reading to learn more about “what is white light?”.
Table of Contents
How does Prism work?
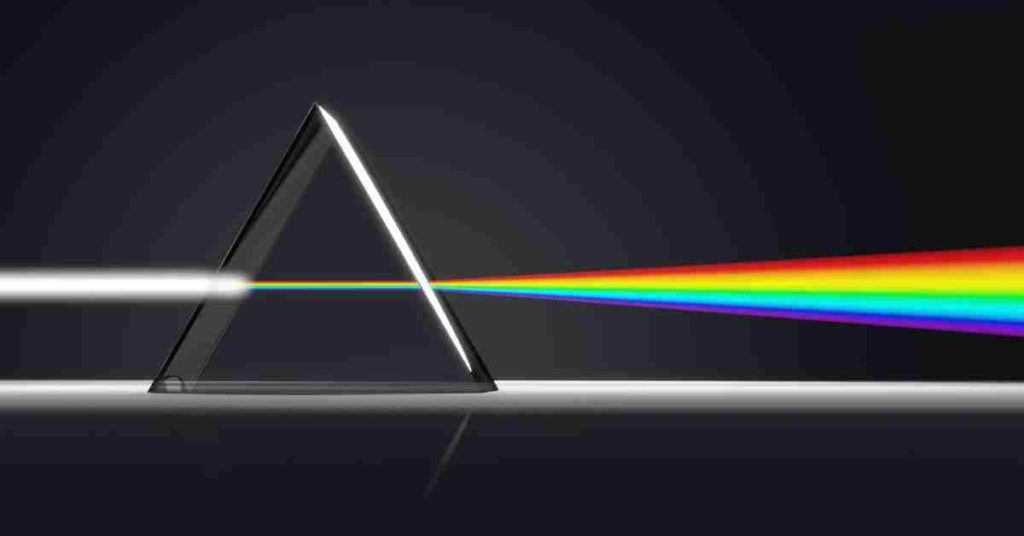
When white light travels through a transparent material (such as air) into another (such as glass), its components deflect the first time based on their color, and then again when they reemerge (back into the air, for example). This results in a rainbow-like dispersion of colorful light beams from red to violet.
The Working Principle of Prism
A simple triangular prism can split white light into a spectrum of its constituent colors.
As light passes through the prism, each color or wavelength that makes up white light bends or refracts differently; the shorter wavelengths (those at the violet end of the spectrum) bend the most, while the longer wavelengths (those near the red end of the spectrum) bend the least.
Refraction of Light
When white light enters a prism, it is twisted, or refracted, and split into its constituent wavelengths.
Each wavelength of light has a unique color and bends at a unique angle. The colors of white light always emerge in the same order via a prism: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Key Points
- White light is a combination of all colors (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet) in nearly equal proportions.
- The Sun is its main source of white light.
- Photons are the particles that light is made up of, which are like tiny packets of energy.
- The exact speed of light in a vacuum is 299,792 kilometers per second.
- The rate at which light is emitted by the source is called the intensity of light.
- The number of crests that pass through a specific point in a second is known as light frequency.
- The distance between two consecutive crests or troughs is known as the wavelength of light.
- Light waves travel at the same speed in a vacuum.
Historial Fact about White Light
During one of his optical experiments in 1666, Newton transmitted sunlight through a prism, splitting the light beam into multiple colors, similar to what he saw around the borders of his optical lenses. Newton was the first to realize that white light comprises a mixture of light rays, each of which has a distinct color.
Light Energy
Light energy is a type of energy that can be seen with the naked eye and has a wavelength of 400–700 nanometers. Hot things, such as lasers, lights, and the sun, emit an electric pulse known as light.
Photons are the small energy packets that constitute light.
Luminous Flux
The luminous flux of a light source is a measure of its brightness in terms of energy emitted. The SI unit for measuring light flux is the lumen (lm). It is a measurement of the energy emitted in the form of visible light by a light-producing source. A typical criterion for comparing light bulbs is luminous flux.
Luminous flux is also known as luminous power.
Related Links
Heat Flux-An Overview
Electromagnetic Force
Electric Field Units & Definition
Momentum Equation| Definition and Examples
Frequency Simple Definition & Examples
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a prism?
In optics, a prism is a piece of glass or other transparent material cut with exact angles and plane sides. We use it to analyze and reflect white light.
2. What is a spectrum?
The term “spectrum” refers to the orderly separation of colored beams. The white light spectrum comprises six fundamental colors: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
It is a visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. It is radiant energy that travels in a straight line and can be seen with the naked eye in a specific wavelength.
Temperature is not a form of energy. It is the degree or intensity of heat present in a substance or object.
Photon energy is given by E = hf and is related to the frequency f and wavelength λ of the radiation by
E=hf=hcλ(energy of a photon).
where E is the energy of a single photon and c is the speed of light.
h is Planck’s constant and its value is 4.14 × 10−15 eV · s.
More Interesting Links
Arrhenius Equation Definition & Formula
Is Titanium Magnetic?
Crest of a Wave| Wave Properties
Transverse waves
Light Energy| 5- Easy Examples
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023