Can velocity be negative?: Velocity can be a negative as it’s a vector quantity. A positive velocity indicates that the item is moving in the positive direction as described by the coordinate system, whereas a negative velocity indicates that the object is going in the opposite direction. In simple words, It is that speed in the opposite direction when velocity turns negative.

Table of Contents
What is Velocity?
Speed is the pace at which an object moves along a path in terms of time, whereas velocity is the rate and direction of movement. In other words, while speed is a scalar value, velocity is a vector. For example, 50 km/hr (31 mph) denotes the speed of a car driving along a road, whereas 50 km/hr east denotes the velocity. The scalar magnitude of the velocity is the speed of motion.
Velocity Definition in Simple Words
- Rate of change of the object’s position with respect to a frame of reference and time.
- Displacement of the object in unit time.
- A measure of how fast something moves in a particular direction.
- The quickness of motion or action (simplest velocity definition).
- The measurement of the rate and direction of change in position of an object.

Units
- m/sec (SI unit).
- miles per hour.
- kilometers per hour (kph).
- kilometers per second (km/s).
- foots per second.
What’s the formula for Velocity?
Velocity formula = displacement ÷ time
Displacement = Change in position (final position – initial position).
Time = Total time taken to cover the distance from the initial position to the final position.
Can Velocity be Negative?
Velocity is a vector quantity which means that it has both magnitude and direction. In vectors, the negative sign only represents the direction and nothing else. Positive and negative signs depend upon our choice of the coordinate system.
If an object is moving along a line, positive velocity means, it’s moving in the positive direction defined by the coordinate system, and negative velocity means it’s moving in the other direction.
However, speed is the magnitude of the velocity vector and is always a positive quantity.
Key Points-Velocity

- Rate of change of displacement (mathematical velocity definition).
- Vector quantity.
- SI unit is meter per second (m/sec).
- A body moving with uniform velocity will have zero acceleration.
- The graph of uniform velocity is a straight line.
- A stone is thrown upward with a certain velocity, at maximum height its velocity will be zero.
- The dimensions of velocity are [LT-1]
- Can velocity be Negative? Yes

Types of Velocity
Instantaneous Velocity
The velocity of the body at any instant of time is known as Instantaneous velocity. It is obtained by dividing displacement (x) with a time interval (t), which is very short such that it tends to zero.

Unifrom Velocity
If the velocity of a body changes equally in equal intervals of time, then the body is moving with uniform velocity.
Relative Velocity
When two bodies are in motion then the velocity of one body relative to the other is called relative velocity.
Terminal Velocity
Steady speed achieved by a free-falling object through a gas or liquid is called Terminal velocity. During freefall, a paratrooper attains terminal velocity with which it comes to the ground.

Examples of Velocity
- The speed of a car travelling north on a road.
- Speed of a rocket launching into space.
- A car moving at 75 miles per hour towards East.
- Earth is moving around the sun with a velocity of 30 km/sec.
Negative Velocity- Examples
- By convention the distances measured towards the right of a fixed point are positive and those measured towards the left of the fixed point are negative. In this way, a position 5m means 5m right of the origin and a position -5m means 5m left of the origin.
- If a car is moving away from you (fixed point) then the velocity is positive. If a car is coming towards you (fixed point) then the same vector reverses direction and hence the velocity is negative.
What is Displacement?
Displacement (d) is the shortest distance between the initial position (Xi) and the final position (Xf). It is a vector quantity i.e. it has both magnitude and direction.
Its SI unit is the meter (m).
d = Xf -Xi (m)
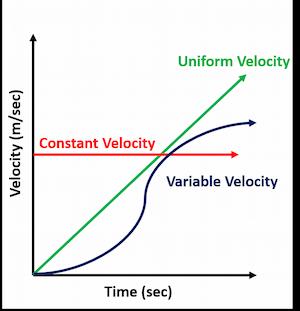
In the velocity-time graph, time is taken along the horizontal axis while the vertical axis shows the velocity of an object. The distance moved by an object can be determined by using a velocity-time graph. It has three different cases:
Case-1 (Constant Velocity)
When the velocity of the body is increasing at a constant rate, then we get a horizontal straight line of the velocity-time graph (shown in red colour in the Figure). An object moving with a constant velocity has a constant speed in a constant direction. In other words, a constant velocity means motion in a straight line at a constant speed.
Case-2 (Uniform velocity)
When the velocity of the body is increasing at a constant rate, we get a straight line which rises the same height for an equal interval of time (shown in green colour in Figure).
Case-3 (Variable Velocity)
When velocity is increasing at a variable rate, then the velocity-time graph will be a curve (shown in dark purple colour in Figure).
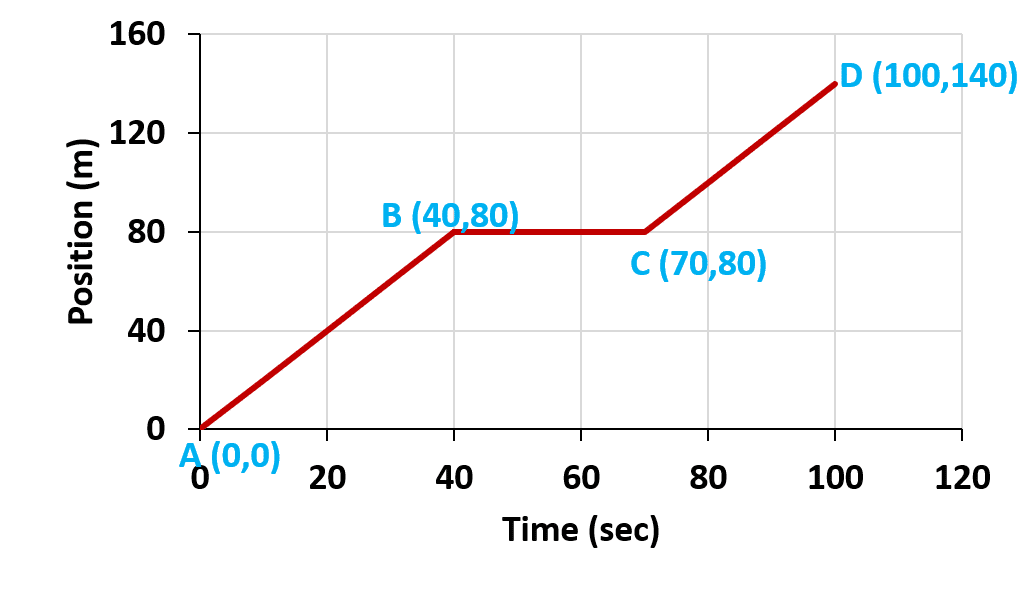
How to find velocity on a position vs time graph
Velocity (v) = slope of position vs time graph.
Slope = changes in y-axis ÷ Changes in the x-axis.
In the position-time graph,
Slope = changes in position ÷ Changes in time.
Sope of line AB = (80-0) ÷ (40-0) = 2.
So “v” from A to B = 2m/sec.
The slope of line BC= (80-80) ÷ (70-40) =0.
Therefore, “v” from B to C = 0m/sec.
The slope of line CD = (140-80) ÷ (100-70) =2.
Similarly, “v” from C to D = 2m/sec.
Difference between Speed and Velocity
| Speed | Velocity |
| Scalar quantity. | Vector quantity. |
| Rate of change of distance (speed definition). | Rate of change of displacement |
| Speed of an object can never be negative. | It can be negative. |
| Distance covered in unit time. | Displacement covered in unit time. |
| Does not involve direction. | Involves direction. |
| 10 km/hr (6.21 mph) describes the speed. | 10 km/hr (6.21 mph) east describes the velocity. |
| Can speed be negative? No its a scalar quantity. | Can velocity be negative? Yes, it’s a vector quantity. |
Quick Links
Example problems
Example 1: A Cyclist completes a half-round of a circular track of radius 318m in 1.5 minutes. Find its speed and velocity.
The radius of track r = 318m
Time taken = 1min and 30 seconds = 90 seconds.
Displacement = 2r = 2(318m)=636 m.
v= displacement/time taken
v=636m/90sec =7.07m/sec.
Example 2: The value of velocity (v) and time is 1.5 m/s and the time taken is 100 seconds. Find the value of displacement.
v = displacement ÷ time.
1.5 = d ÷ 100
d = 1.5 × 100 = 150 m
Summary
- Velocity can be a negative as it’s a vector quantity.
- A positive velocity denotes that the object is traveling in the positive direction as defined by the coordinate system.
- A negative velocity denotes that the object is moving in the opposite direction.
- The velocity formula is displacement divided by time.
- It requires both magnitude and direction to explain.
- Instantaneous velocity is the velocity at any given moment of time.
- Average velocity is the total displacement divided by total time.
- A change in velocity indicates acceleration.
Related Topics
Momentum Equation| Definition and Examples
Centripetal Acceleration| Examples
Mechanical Energy Formula & Examples
Light Energy| 5- Easy Examples
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the frequently asked questions are listed below:
1. Can work be negative?
When a force operating on a body displaces it in the direction of a force, work is done. When a force of 1 Newton is applied over a distance of 1 metre, the work done by a moving object equals 1 Joule. Because the applied force can be either negative or positive, work can also be either negative or positive.
Negative work can be seen in the motion of a body against a force of friction.
2 Can force be negative?
The force will be negative if the applied force is in the opposite direction as the displacement of the moving object. Positive forces are those that are oriented in the positive direction.
Forces oriented to the left are commonly referred to as negative forces.
3. What is difference between mass and weight?
A body’s mass is the amount of substance it contains, whereas its weight is equal to the force with which the earth draws it. Mass, unlike weight, is a scalar quantity that can never be zero.
4. Can displacment be negative?
Displacement can be negative since it is a vector quantity that depends on magnitude and direction.
The negative sign indicates the direction.
Check the full article “can displacement be negative?”.
5. Can momentum be negative?
Momentum is a vector quantity that is calculated by multiplying the mass of an item by its velocity. If the item’s velocity is negative, i.e. the object is travelling in the negative direction, the momentum will be negative as well. Check the full article “can momentum be negative?”.
1 km = 1000 m.
1 m = 0.001 km.
1 hour = 3600 secs.
1 sec =1/3600 hours.
1m/sec =0.001 km x 3600/hour
=3.6 km/hour
1 km/hour=1000m/60×60 =10/36 m/sec
Yes, velocity is a vector quantity. It depends upon the speed and direction of a moving object. The direction of movement can be positive or negative.
Author
Umair Javed
Umair has been working at Whatsinsight since 2020 as a content writer.
He has a Masters degree in Material Science.
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023