Secondary energy sources, also known as energy carriers, are generated by transforming primary energy sources like solar, wind and hydro energy. They transmit usable energy from one point to another. Common examples of secondary energy sources are petrol, hydrogen and electricity.
Primary energy resources are those found in nature. They include fossil fuels (petroleum, natural gas, and coal), uranium, wind and water, biomass, and solar energy. Secondary energy sources are derived from the transformation of primary energy sources, such as gasoline, which is derived from the processing of crude oil, and electric energy, which is derived from the conversion of mechanical energy (hydroelectric plants, Aeolian plants), chemical plants (thermoelectric), or nuclear energy (nuclear plants). Electric energy is generated by electric plants, which are suitable installations capable of converting primary energy (non-transformed) into electric energy.
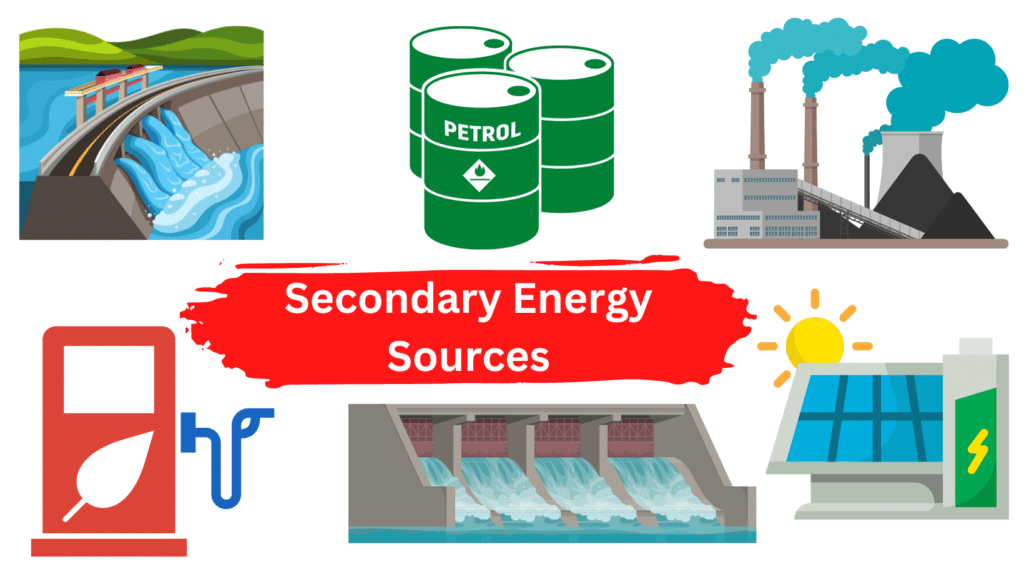
Table of Contents
Examples of Primary Energy Sources
Natural primary energy sources exist and have some stored energy capacity. Once energy is processed or converted from one form to another, it is no longer a primary energy source.
- oil
- kerosene
- coal
- Nuclear material for fission
- Geothermal (Heat from the Earth’s crust)
- Hydroelectric (Energy stored in water higher than a set of turbines)
- Solar power (Radiation energy from the Sun)
- Tidal power (Kinetic energy contained within the tides)
- Wind power (Kinetic energy contained within the wind)
Examples of Secondary Energy Sources
Secondary energy sources come from the use or processing of primary energy sources. Electricity, heat and biofuel are common examples. Some more examples are listed below:
- Stored gravitational energy from water is converted into electricity in a hydroelectric plant;
- Oil is refined to produce petrol that can be used to power a car;
- Coal is burnt to produce heat on the fire.
More Links
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023