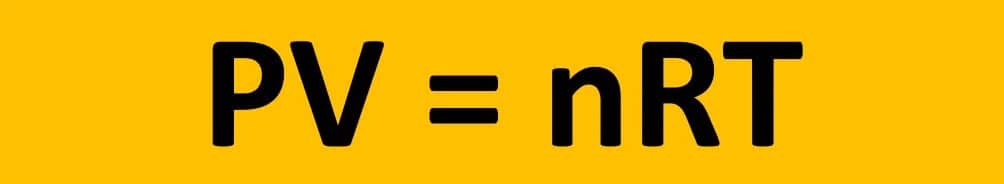The quantity of energy transferred from one system to another is called thermodynamic work in thermodynamics. It is a generalisation of the mechanical work concept in mechanics. Work is measured in joules in the SI measurement system (symbol: J). Power is the rate at which work is completed.
The equation is:
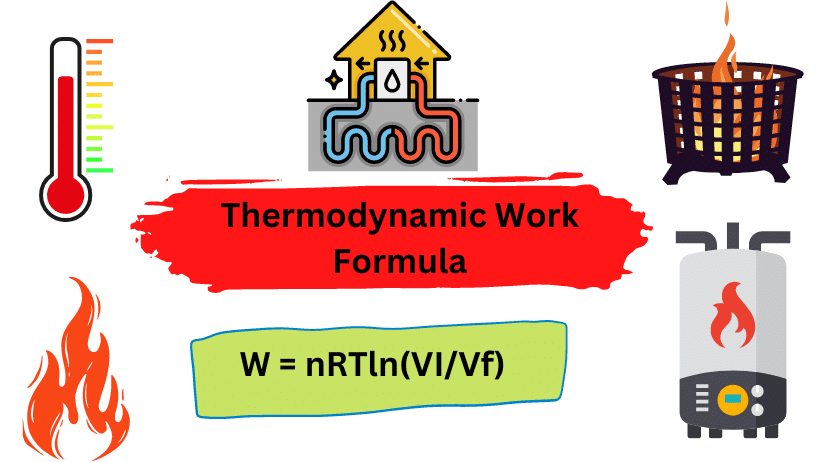
W = nRTln(Vi/Vf)
Where:
- W: Thermodynamic work
- R: Ideal gas constant. (8.314 kg*m2/s2*mol*K)
- T: Absolute Temperature in Kelvin.
- n: moles
- Vi: Initial volume
- Vf: the final volume
Work (W) is defined as the product of force F acting over a distance s:
W = F * s
Pressure = force/area = F/A
Volume = length x area = s x A
W = (P x A) x V/A
W = P x V
The above equation shows that Work in gas is defined as the product of pressure p and volume V during a volume change.
The pressure here is applied from the outside of the gas; the positive work results from the piston moving in such a way that it reduces the volume of the gas, introducing a negative sign to the work relation.
W= -PV
where:
- W is the work done on or by a system;
- P is the pressure;
- ΔV is the change in volume of the system.
The negative sign in the equation indicates that work is done by the system when the volume increases (expansion), and work is done on the system when the volume decreases (compression). The unit of work in the SI system is joule (J).
To do work on a gas, its volume must be reduced; to have work done by a gas, its volume must be increased. In general, when a state changes, both the volume and the pressure change. As a result, it is more accurate to define work as the integrated, or summed variable pressure times the volume change from State 1 to State 2.
W =−Vi∫VfPdV
If P is a constant (that is if the process of changing the volume of the gas is isobaric), then P can simply be removed from the integral to regenerate the previous relationship:
W =−P (Vi∫VfdV) = -PΔV
From ideal gas law: PV = nRT
W =−nRT/V x (Vi∫VfdV) =nRT (Vi∫Vf (dV/V) =−nRTlnVf/Vi
Removing the negative sign by swapping the integral’s limits
W = nRTln(Vi/Vf)
More Links
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023