Aluminum is the most abundant metal on the planet and one of the most affordable. Aluminium is the third most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, and it forms strong bonds with other elements as well. That is, it does not exist as a pure metal in nature. Aluminum nucleus consists of 13 protons and 14 neutrons. 13 electrons occupy available electron shells.
The first two electrons in an aluminium electron configuration will be in the 1s orbital.
Since the 1s orbital can only hold two electrons, the next two electrons for aluminium will fill the 2s orbital.
The remaining six electrons will fill the 2p orbital. The p orbital can accommodate six electrons. These six electrons will be placed in the 2p orbital, followed by two electrons in the 3s orbital. Since the 3s is now full, we’ll move to the 3p and place the remaining electron there. As a result, the Aluminium electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 and is seen in the image below.
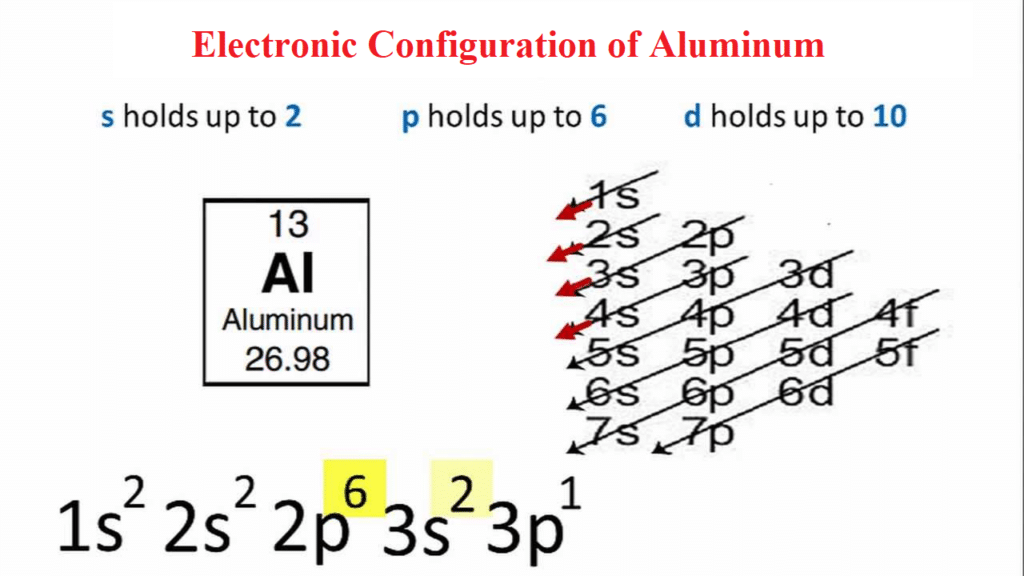
Table of Contents
Aluminum- Key Points
| Name of element | Aluminum (Al) |
| Atomic number | 13 |
| Molar mass | 26.982 g/mol. |
| Aluminum electron configuration | 1s22s22p63s23p1 |
| Density | 2.7 g/cm³ |
| Melting point: | 660.3 °C |
| Boiling point: | 2,470 °C |
Element Aluminum
Aluminium is a very light metal, weighing one-third the weight of steel or copper. Aluminium is easy to recycle and corrosion resistant; it oxidises similarly to iron, but the oxide actually sticks to the metal and protects the surface. The metal is only one-third the density of steel.
The Bohr model for aluminum shows its 13 protons and neutrons inside the nucleus with 13 electrons orbiting in 3 energy levels.
Summary
- Aluminum is a chemical element. Its symbol is Al.
- it is almost impossible to find pure aluminum in nature because it is such a highly reactive element
- Aluminum is not a magnetic material
- Aluminum’s atomic number in the periodic table of elements is 13.
- The electron configuration of Aluminum is 1s22s22p63s23p1
Related Topics
Neon Element| Properties & Uses
Sulfur trioxide (SO3)
Electron Configuration for Calcium
Sulfur Electron Configuration and Molar Mass
Titanium Electron Configuration
Recommended Video
More Interesting Links
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023