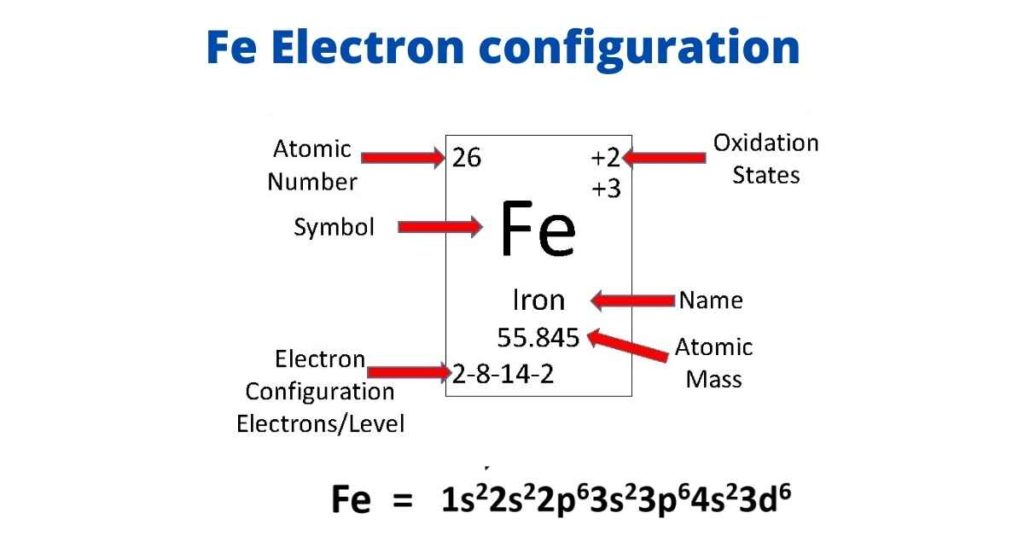
Iron is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust in terms of mass. It has the atomic number 26 and the chemical symbol Fe (from the Latin word “Ferrum”). In four different shells around the nucleus, a neutral iron atom contains 26 protons, 30 neutrons, and 26 electrons. The Earth’s core is thought to be mostly iron, with a little nickel and sulfur thrown in for good measure. The iron’s electron configuration is 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6.
Valence electrons are a single outer shell electron in an atom’s outer shell that is responsible for the atom’s chemical characteristics. In other words, a valence electron is an atom’s electron that may be transferred to or shared with another atom and is placed in the atom’s outermost shell.
| Name of element | Iron |
| Atomic mass | 55.85 g.mol -1 |
| Density | 7.8 g.cm-3 at 20°C |
| Characteristics | ductile, grey, relatively soft metal and is a moderately good conductor of heat and electricity. |
| Melting point | 1536°C |
| Molar mass | 55.845 grams/mol |
Table of Contents
Summary
- Iron is a nonmetal with a mass number of 14 and an atomic number of 7.
- Iron has eight valence electrons.
- The electronic configuration of iron is 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6.
- The molar mass of iron is 55.84 grams/mol.
Related Topics
How many electrons does oxygen have?
SiO2 Lewis Structure| Step By Step Construction
Sulfur Electron Configuration
Electron Configuration for Calcium
Recommended Video
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is titanium magnetic?
Titanium, being a paramagnetic substance, is only weakly attracted to magnets. The presence of four unpaired electrons in its electrical structure is the primary cause of its paramagnetic characteristics (check full article: is titanium magnetic?).
2. Is aluminum magnetic?
Aluminum (United States English), also known as Aluminum (British English), is not magnetic under normal conditions, owing to its crystal structure. Along with other metals like magnesium and lithium, it’s classified as a paramagnetic substance.
In other words, aluminum is not magnetic; nevertheless, in the presence of an external magnetic field, aluminum becomes “slightly” magnetic as its electron aligns with the magnetic field.
3. What is the density of water g/ml?
This density of water is equal to a rounded value of 1 gram per milliliter (g/ml) or 1 gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm3). (Check the full article to know the accurate value of the density of water in g/ml)
4. How many neutrons are in hydrogen?
The vast majority of hydrogen atoms lack neutrons, making them the lightest atoms possible with only one electron and one proton (check full article How Many Neutrons Does Hydrogen Have?)
6. How many electrons does iron have?
Iron contains eight valence electrons. Because iron is a transition metal, electrons in its d subshells can be used as valence electrons. Valence electrons are electrons that exist outside of a noble-gas core in a transition metal. Iron has the electrical configuration 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6.
7. What’s the molar mass of Aluminum?
Aluminum molar mass is 26.982 g/mol.
8. How many electrons does oxygen have?
A single oxygen atom has eight protons, eight electrons, and eight neutrons.
Oxygen is a stable isotope of oxygen with a nucleus of 8 neutrons and 8 protons. Its mass is 15.99491461956 u. Check the full topic “How many electrons does oxygen have?”.
9. How cold is liquid nitrogen?
Liquid nitrogen is nothing more than extremely cold nitrogen. The temperature is 320 degrees Fahrenheit below zero (-196oC). It’s so cold that anything it comes into contact with instantly freezes.
Check the full article “How cold is liquid nitrogen?”.
More Interesting Topics
The pH of Distilled/ De-Ionized Water
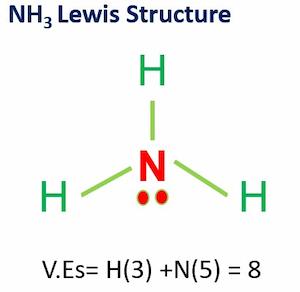
NH3 Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Is Nh3 Polar?
N2O Lewis Structure| Nitrous oxide-Laughing Gas
HCN Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry
Neon Element| Properties & Uses
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023