A steric number is a number used to express regions of electron density surrounding a particular atom.
In simpler terms, the steric number represents the number of lone pairs and atoms bonded to the central atom of a molecule.
Table of Contents
Examples of Steric Number
Steric Number of CO2
If we study Lewis structure of CO2, carbon forms a double bond to each of the two oxygen atoms to produce a small symmetrical, linear molecule of CO2.
CO2 has a linear molecular geometry because Oxygen atoms form sigma bonds with the central carbon atom to complete their octet. As a result, there are no lone pairs of electrons, but bonding pairs of electrons also repel each other.
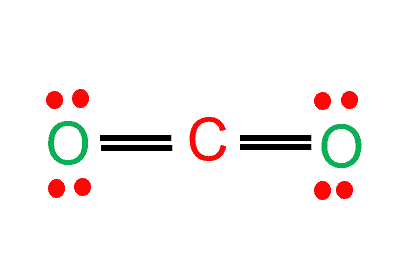
In a CO2 molecule, the center atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms and has no lone pairs, implying that its steric number is equal to 2.
Steric Number of NH3
In ammonia molecular geometry, three hydrogen atoms are bonded to a nitrogen atom in the middle.
Nitrogen has 5 electrons in the valence shell, so it needs to combine with 3 hydrogen atoms to fulfill the octet rule.
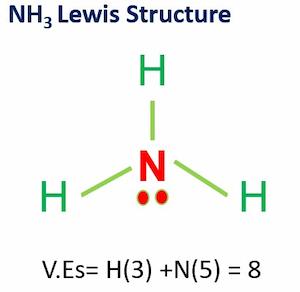
Since nitrogen is bonded to three hydrogen atoms and has one lone pair of electrons on it, which implies that its steric number will be equal to
SNnitrogen=3+1=4
Examples of Steric Number
| Molecule | Number of Atoms | Steric Number | Explanation | Structure |
| Methane (CH4) | 5 | 4 | Methane has one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom contributes one bond, and there are no lone pairs on the carbon atom. Therefore, the steric number is 4. | tetrahedral |
| Ammonia (NH3) | 4 | 4 | Ammonia has one nitrogen atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom contributes one bond, and there is one lone pair on the nitrogen atom. Therefore, the steric number is 4. | trigonal pyramidal |
| Water (H2O) | 3 | 4 | Water has one oxygen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom contributes one bond, and there are two lone pairs on the oxygen atom. Therefore, the steric number is 4. | bent |
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | 3 | 2 | Carbon dioxide has one carbon atom double bonded to two oxygen atoms. Each oxygen atom contributes one bond, and there are no lone pairs on the carbon atom. Therefore, the steric number is 2. | linear |
| Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) | 7 | 6 | Sulfur hexafluoride has one sulfur atom bonded to six fluorine atoms. Each fluorine atom contributes one bond, and there are no lone pairs on the sulfur atom. Therefore, the steric number is 6. | octahedral |
| Phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) | 6 | 5 | Phosphorus pentachloride has one phosphorus atom bonded to five chlorine atoms. Each chlorine atom contributes one bond, and there are no lone pairs on the phosphorus atom. Therefore, the steric number is 5. | trigonal bipyramidal |
| Iodine heptafluoride (IF7) | 8 | 7 | Iodine heptafluoride has one iodine atom bonded to seven fluorine atoms. Each fluorine atom contributes one bond, and there are no lone pairs on the iodine atom. Therefore, the steric number is 7. | pentagonal bipyramidal |
| Ethylene (C2H4) | 6 | 2 | Ethylene has two carbon atoms double bonded to each other and each carbon atom is also bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Each carbon atom contributes two bonds and there are no lone pairs. Therefore, the steric number is 2. | planar (with a double bond between the carbon atoms) |
| Acetylene (C2H2) | 4 | 2 | Acetylene has two carbon atoms triple bonded to each other and each carbon atom is also bonded to one hydrogen atom. Each carbon atom contributes three bonds and there are no lone pairs. Therefore, the steric number is 2. | linear (with a triple bond between the carbon atoms) |
Significance of Steric Number
Steric number is a concept used in chemistry to describe the number of atoms bonded to a central atom in a molecule or ion, including both bonded atoms and lone pairs. The steric number is significant for several reasons:
- Geometry: The steric number is closely related to the geometry of a molecule. For example, molecules with a steric number of 4 typically have a tetrahedral geometry, while molecules with a steric number of 5 typically have a trigonal bipyramidal geometry.
- Bond angles: The steric number also determines the bond angles between the atoms in a molecule. For example, a molecule with a steric number of 4 has bond angles of approximately 109.5 degrees, while a molecule with a steric number of 5 has bond angles of approximately 90 degrees and 120 degrees.
- Hybridization: The steric number is related to the hybridization of the central atom. For example, a molecule with a steric number of 4 has a central atom that is typically sp3 hybridized, while a molecule with a steric number of 5 has a central atom that is typically sp3d hybridized.
- Reactivity: The steric number can also affect the reactivity of a molecule. For example, molecules with larger steric numbers may be less reactive than those with smaller steric numbers due to the increased steric hindrance.
- Polarity: The steric number can also affect the polarity of a molecule. For example, molecules with a steric number of 2, such as linear molecules, are typically nonpolar, while molecules with higher steric numbers, such as tetrahedral molecules, may be polar.
Overall, the steric number provides important information about the geometry, hybridization, and reactivity of molecules, which is useful in predicting their properties and behavior in chemical reactions.
Frequently Asked Questions
| Number | Question | Answer |
| 1 | What is steric number? | The steric number is the number of atoms bonded to a central atom in a molecule or ion, including both bonded atoms and lone pairs. |
| 2 | How is steric number related to molecular geometry? | The steric number is closely related to the molecular geometry of a molecule. For example, molecules with a steric number of 4 typically have a tetrahedral geometry, while molecules with a steric number of 5 typically have a trigonal bipyramidal geometry. |
| 3 | How is steric number related to hybridization? | The steric number is related to the hybridization of the central atom. For example, a molecule with a steric number of 4 has a central atom that is typically sp3 hybridized, while a molecule with a steric number of 5 has a central atom that is typically sp3d hybridized. |
| 4 | Can steric number affect the reactivity of a molecule? | Yes, steric hindrance caused by larger steric numbers can affect the reactivity of a molecule. Molecules with larger steric numbers may be less reactive than those with smaller steric numbers due to the increased steric hindrance. |
| 5 | How does steric number affect polarity? | The steric number can also affect the polarity of a molecule. For example, molecules with a steric number of 2, such as linear molecules, are typically nonpolar, while molecules with higher steric numbers, such as tetrahedral molecules, may be polar. |
| 6 | Can steric number be used to predict bond angles? | Yes, the steric number can be used to predict the bond angles between atoms in a molecule. For example, a molecule with a steric number of 4 has bond angles of approximately 109.5 degrees, while a molecule with a steric number of 5 has bond angles of approximately 90 degrees and 120 degrees. |
| 7 | How is steric number determined experimentally? | The steric number is typically determined experimentally using techniques such as X-ray crystallography or electron diffraction, which can provide information about the arrangement of atoms in a molecule. Alternatively, it can be determined using theoretical methods such as molecular orbital theory or valence bond theory. |
More Links
Charge of Ammonia (NH3)| Simple Steps
HCl Intermolecular Forces| Dipole-Dipole Forces
CH4 Polarity| Simple Explanation
Sigma Bond- Definition & Explanation
Is O2 Polar or Nonpolar?
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023



