Bioenergy is defined as biomass-derived energy. Biomass is the material burned or processed to produce bioenergy. It is composed of organic material derived from living organisms such as plants and animals. Some examples of bioenergy are listed below:
- Burning wood to create heat.
- Using biodiesel and ethanol to fuel vehicles.
- Using methane gas and wood to generate electricity.
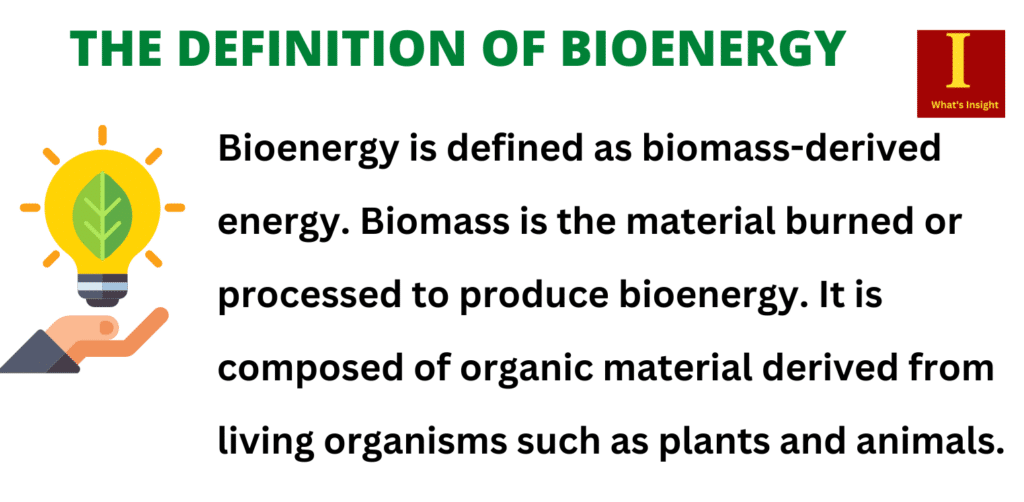
Table of Contents
Bioenergy Definition
Bioenergy is derived from biological sources, such as living organisms and their metabolic products. It could take the form of heat, light, electricity, or transportation fuel. Another commonly used (and often interchangeable) term is biofuel, which refers to fuel derived from biological sources. The biological sources that are used to produce bioenergy are known as biomass.
What is Biomass?
Some sources of biomass are listed below:
- Wood (including wood chips, sawdust, and forestry by-products)
- Algae purpose-grown plants animal fat waste cooking oil (energy crops)
- Sewage from livestock (including dairy)
Why Bioenergy Is Important?
Bioenergy is a renewable source of energy that has the potential to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Land use and greenhouse gas emissions are the two most significant environmental impacts of bioenergy.
Biodiesel and Bioethanol Definitions
- Biodiesel: Biodiesel is a type of fuel that is created by extracting oils or fats from plants or animals directly. Esters, which behave similarly to regular diesel, are created chemically. Biodiesel can be used alone or mixed with regular diesel. The most common sources of oil for biodiesel are waste cooking oil or specially grown plants.
- Bioethanol: A type of alcohol that is produced primarily from carbohydrates produced in sugar- or starch-bearing plants such as corn, sugarcane, sweet sorghum, or lignocellulosic biomass by microbial fermentation.
Biomass Facts
- The term biomass refers to a wide range of materials, including various types of wood, agricultural residues, and animal and human waste. Several methods exist for converting biomass into electricity.
- Biomass is a renewable energy source because it can always be regrown as long as humans do not devastate the environment through pollution and other activities.
- When biomass is burned, it emits carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas. However, plants (a source of biomass energy) capture nearly the same amount of CO2 as is released when biomass is burned, making biomass a carbon-neutral energy source.
- Biogas and biomass are two different kinds of biofuels. The primary distinction between biomass and biogas is that biomass is a solid material, whereas biogas is a gaseous compound produced by the Anaerobic Digestion process.
- Biogas is a gas with a high energy content that is produced by anaerobic decomposition or thermochemical conversion of biomass.
Related Links
Chemical Reactions| Examples in Daily Life
Condensation Definition| Chemistry
Thermal Energy Equation- Simple Overview
Is Cotton Biodegradable?-Short Answer
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What Does Bioenergy Mean?
Bioenergy refers to the chemical energy stored in organic materials that can be converted into direct, usable energy sources via biological, mechanical, or thermochemical processes.
2. Feedstocks?
The term “feedstock” refers to any material that is used to make fuel. Biomass feedstock, which is material from algae, plants, and animals used to produce biofuels, is a common type of feedstock in renewable fuel production.
3. Combustion reaction?
Combustion is a chemical reaction that results in the production of heat and light. The majority of combustion occurs when the gas oxygen reacts with another substance.
4. What is biogas?
Biogas is a renewable fuel made from the decomposition of organic matter like food scraps and animal waste. It has numerous applications, including vehicle fuel, heating, and electricity generation.
5. What are energy crops?
The energy crops are feedstocks for the bioenergy value chain, which uses anaerobic digestion to produce heat and electricity from biomass/biogas. Sugarcane, sugar beet, potato, tapioca, and maize are among the various energy crops.
More Links
References
- http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/5369284.stm
- http://www.bioenergy.org.nz/bioenergyinfo.asp#whos_who
- http://www.bioenergy.org.nz/documents/publications/banz/freq_questions.pdf
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023