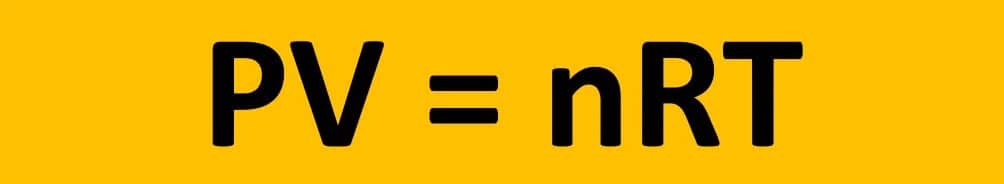Most wind turbines are built with rotor-mounted blades resembling aeroplane propellers. When air passes through them, the rotor turns a shaft, which powers an electrical generator. In an ideal world, a wind turbine would convert 100% of the wind that passes through its blades into power. However, due to friction, these wind turbines only have efficiency ratings ranging from 30% to 50% of the rated power output.
The following formula is used to calculate power output:
Power of wind turbines= [air density×swept area of blades×wind speed3]/2
Where the area is in meters squared, air density is in kilograms per meter cubed and wind speed is in meters per second. The above equation shows that the ability of a wind turbine to generate the maximum amount of power can depend on the wind. Wind farms are carefully planned to be located in areas with consistent wind all year.
Working Principle of wind turbines
Wind causes wind turbine blades to rotate. However, this does not have to be a strong wind: most turbine blades will start turning at a wind speed of 3-5 metres per second, which is a gentle breeze.
This spinning motion turns a shaft in the nacelle (the box-like structure on top of a wind turbine). The kinetic energy of the turning shaft is then converted into electrical energy by a generator built into the nacelle. This is then routed through a transformer, which raises the voltage so it can be transported on the National Grid or used locally.
The faster the wind blows, the more electricity is generated up to a certain point. In fact, doubling the wind speed generates up to eight times more electricity.
More Links
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023