The process when a gaseous substance changes states to become a solid is called deposition. Gas is a state of matter which contains molecules with a high amount of kinetic or moving energy, and they vibrate very quickly. A solid has particles that have less kinetic energy and vibrate at a slower rate without changing position.
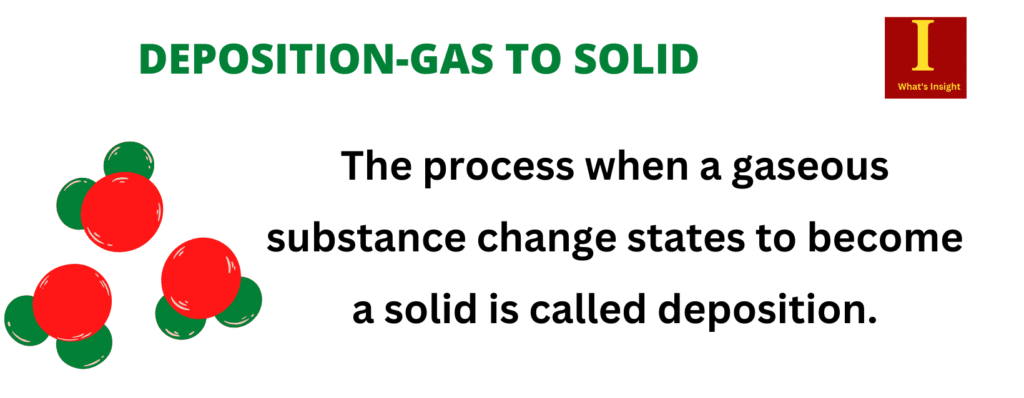
The gaseous substance may get deposited as a crystal bypassing the intermediate liquid state. A common gas-to-solid conversation example is the formation of frost, which occurs when water vapour (gaseous form) in the atmosphere changes directly into ice. The deposition process is the opposite of sublimation.
Table of Contents
Examples of Gas to Solid
- Making dry ice or solid carbon dioxide involves removing gaseous carbon dioxide from the air and causing the gas particles to skip the liquid phase and deposit into a solid to form a chunk of dry ice using cold temperatures and higher pressure.
- A carbon dioxide fire extinguisher is filled with gaseous carbon dioxide, but the higher pressure inside the canister causes this to turn into solid carbon dioxide, which is then released as a white powder when used to extinguish a fire.
- The deposition process is important in many manufacturing technologies, such as semiconductor manufacturing. Solid alloys are heated to a gaseous state before being sprayed onto objects such as semiconductors in this process. The heat energy is lost when the spray hits the semiconductor, and the gaseous substance solidifies into a metal alloy.
Sublimation Process
Sublimation is a solid-to-gas transformation. Dry ice is one of many sublimation examples (frozen carbon dioxide). When dry ice is exposed to air, it changes directly from a solid to a gaseous state (fog).
In general, converting a solid to a gaseous state necessitates an intermediate liquid state.
Sublimation, on the other hand, occurs when solid molecules absorb heat and directly change to a gaseous state. This process involves a physical change of state rather than a chemical reaction.
More Links
| How cold is Liquid Nitrogen? | Condensation Definition| Chemistry |
| What is a Volatile Substance?| Easy Examples | Distillation| Principles, and Processes |
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023