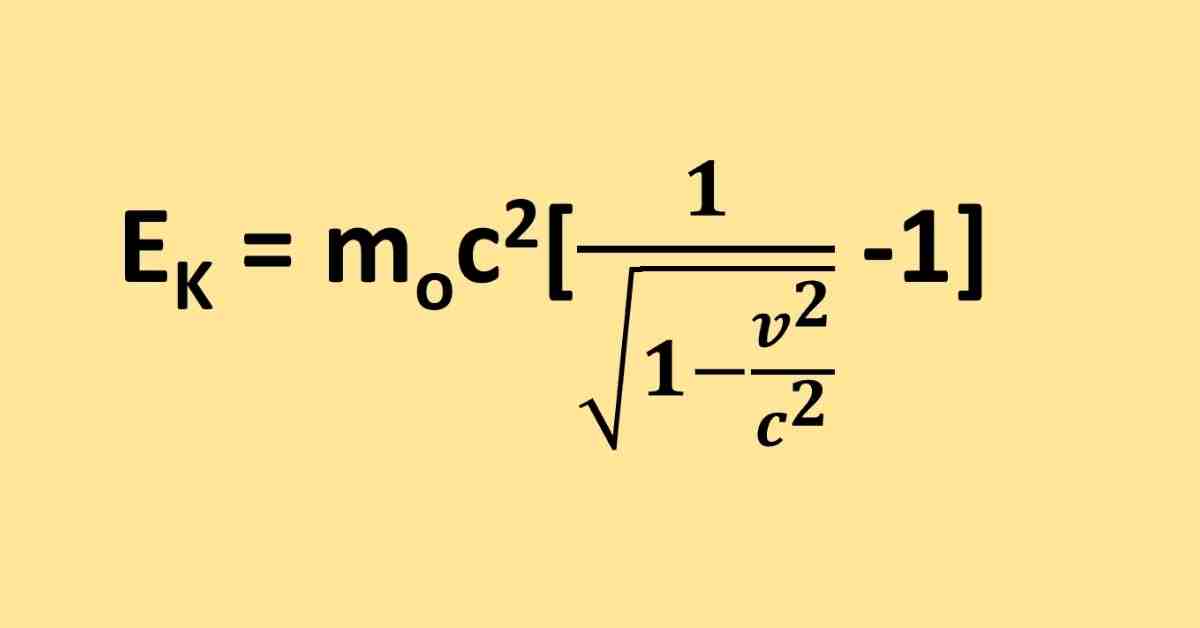The Bohr radius, denoted by the letter a, is the average radius of an electron’s orbit around the nucleus of a hydrogen atom in its ground state (lowest-energy level). The radius is approximately equivalent to 5.29177 x 10 -11 meters, which is a physical constant (m).

In other words, the Bohr radius (a) is a physical constant that represents the most probable distance between the nucleus and the electron in a hydrogen atom in its ground state (non-relativistic and with an infinitely heavy proton).
It is named after Niels Bohr, due to its role in the Bohr model of an atom.
Table of Contents
Bohr Radius in Simple Words
The Bohr radius is a measure of the size of an atom. Here is an explanation of what the Bohr radius is and what it means, simplified for kids:
- Atoms are made up of a central nucleus and electrons that orbit around the nucleus.
- The Bohr radius is the distance from the nucleus to the electron in the lowest energy level (also called the ground state).
- It is named after Niels Bohr, a scientist who studied atoms and their structure.
- The Bohr radius is a very small distance, about 0.0000000000529 meters.
- This distance is important because it determines the size of the atom and how it interacts with other atoms and molecules.
- The smaller the Bohr radius, the smaller the atom, and the more tightly the electrons are held by the nucleus.
- The Bohr radius is used in many calculations and formulas in physics and chemistry to describe the behavior of atoms.
- Understanding the Bohr radius helps scientists understand the behavior of matter on a very small scale, which can lead to new discoveries and inventions.
Key Points
- An electron’s ground state, or the energy level it typically occupies, is the state with the lowest energy for that electron.
- There is also a maximum amount of energy that an electron can have while still being a component of its atom. Beyond that energy, the electron is no longer linked to the atom’s nucleus and is termed ionized.
- An electron is in an excited state when it momentarily occupies an energy state larger than its ground state. An electron can get excited if it receives more energy, as when it absorbs a photon, or packet of light, or when it collides with a neighboring atom or particle.
- To be boosted to a higher energy orbital, an electron must overcome the energy difference between the orbital it is in and the orbital to which it is heading. This implies it must absorb a photon with exactly that amount of energy or take exactly that amount of energy from another particle in a collision.
- Electrons do not remain excited for long; they quickly revert to their ground states, releasing a photon with the same energy as the one received.
- Transitions between orbitals are unique for each element because the energy levels in the nucleus are defined individually by the protons and neutrons.
- When electrons of a particular atom return to lower orbitals from excited states, the photons they produce have energy that is unique to that atom.
- This provides each element a unique fingerprint, allowing the elements present in a container of gas or even a star to be identified.
Frequently Asked Questions
| No. | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | What is the Bohr radius? | The Bohr radius is the distance between the nucleus and the electron in the ground state of a hydrogen atom. It is denoted by the symbol ‘a0’. |
| 2 | How is the Bohr radius calculated? | The Bohr radius can be calculated using the equation: a0 = (4πε0h^2)/(m_e e^2), where ε0 is the electric constant, h is the Planck constant, m_e is the mass of the electron, and e is the elementary charge. |
| 3 | In what context is the Bohr radius used in physics? | The Bohr radius is used in atomic physics to describe the size of an atom or ion, particularly hydrogen-like atoms. It is also used in quantum mechanics to describe the behavior of electrons in atoms. |
| 4 | What is the significance of the Bohr radius? | The Bohr radius is significant because it is a fundamental constant that describes the size of an atom or ion. It is also used in various calculations related to atomic structure and the behavior of electrons in atoms. |
| 5 | How does the Bohr radius relate to the hydrogen atom? | The Bohr radius is the distance between the nucleus and the electron in the ground state of a |
6. Atomic radius definition?
An atom’s atomic radius (r) is defined as one-half the distance (d) between two nuclei in a diatomic molecule.
7. Definition bohr model
According to the Bohr model, electrons in atoms move in circular orbits around a central nucleus and can only orbit stably in fixed circular orbits at a definite range of distances from the nucleus. These orbits, which are also known as energy shells or energy levels, are linked with certain energies.
8. Define ground state
The electron’s ground state is defined as the state when an electron is at its lowest energy level.
More Interesting Topics
Silicon Carbide – An Overview
Sulfur Electron Configuration
CH4 Polarity
Is Titanium Magnetic?
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023