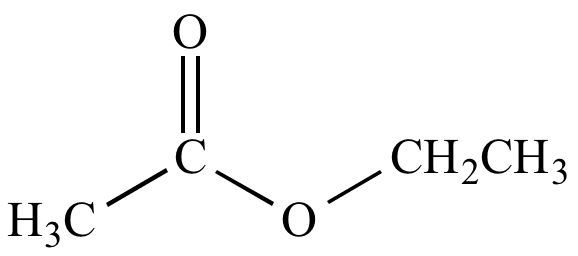
The addition of the CH3CO group to a chemical molecule is known as acetylation. It is the replacement of a hydrogen atom in CH3CO with an active hydrogen atom.
In an acetylation process, the hydrogen atom of an alcohol group is replaced with an acetyl group, resulting in the formation of an ester.
Acetylation of wood is the process of converting free hydroxyl groups in the wood to acetyl groups. This is accomplished by reacting the wood with acetic anhydride, a derivative of acetic acid. As a result, wood’s structure is permanently altered.
Wood’s naturally occurring free hydroxyl groups absorb and release water in response to the environment. Enzymes begin their digestion of wood at the free hydroxyl sites, which is one of the reasons why wood is susceptible to fungal deterioration.
When hydroxyl groups become acetyl groups, the capacity of wood to absorb water declines. As a result, wood is no longer digestible by wood decomposers.
Table of Contents
More Links
Molar Mass of Acetic Acid| Easy-Explanation
The pH of Distilled/ De-Ionized Water
The Specific Gravity of Water
Is Water a Mixture?
Weight of water
Absolute Alcohol| Definition, and Formula
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023