The normal force is a force that we encounter in our daily lives when an object is placed on a surface and the surface exerts a push against it. For instance, when a person is standing on the ground, the normal force keeps them from sinking into the ground. Although gravity is pulling the person downward, the normal force counteracts this force by pushing them upwards. This force is referred to as the normal force and it acts perpendicular to the surface.
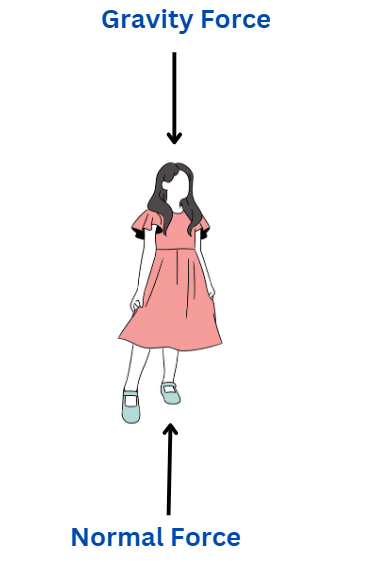
Table of Contents
Formula for normal force
Assuming the object is at rest or moving with constant velocity, the normal force will be equal and opposite to the force exerted on the object by the surface. The formula for normal force is:
Normal force = mass x acceleration due to gravity x cosine(theta)
where:
- Mass (kg)
- Acceleration due to gravity (approx. 9.81 m/s^2)
- Cosine of angle between object and surface (1 if perpendicular, ratio of adjacent side to hypotenuse if on incline)
So the normal force formula can be written as:
Normal force = m x g x cos(theta)
where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and theta is the angle between the object and the surface it is in contact with.
Solved Problem
Problem: A block with a mass of 5 kg rests on an inclined plane that makes a 45-degree angle with the horizontal. Find the normal force acting on the block.
| Formula | Calculation |
| Normal force = mass x acceleration due to gravity x cosine(theta) | |
| Mass = 5 kg | |
| Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s^2 | |
| Theta = 45 degrees | |
| Weight = mass x acceleration due to gravity | Weight = 5 kg x 9.81 m/s^2 = 49.05 N |
| Cosine(theta) = adjacent/hypotenuse | Cosine(45 degrees) = adjacent/hypotenuse |
| Cosine(45 degrees) = 1/sqrt(2) = 0.707 | |
| Normal force = mass x acceleration due to gravity x cosine(theta) | |
| Normal force = 5 kg x 9.81 m/s^2 x 0.707 | Normal force = 34.3 N |
Therefore, the normal force acting on the block is 34.3 Newtons.
More Intersecting Links
Linear Motion or Rectilinear Motion
Linear Acceleration
Uniform Circular Motion| Real-Life Examples
Kinematic Equations| Sample Problems and Solutions
Difference Between Mass and Density
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023