The density of an object is its mass per unit volume. Two objects with the same shape and volume but different masses (for example, two identically sized cubes of wood and iron) have different densities. Density is a physical property of matter that applies to all states of matter (solid, liquid and gas). The density formula is mass divided by volume.
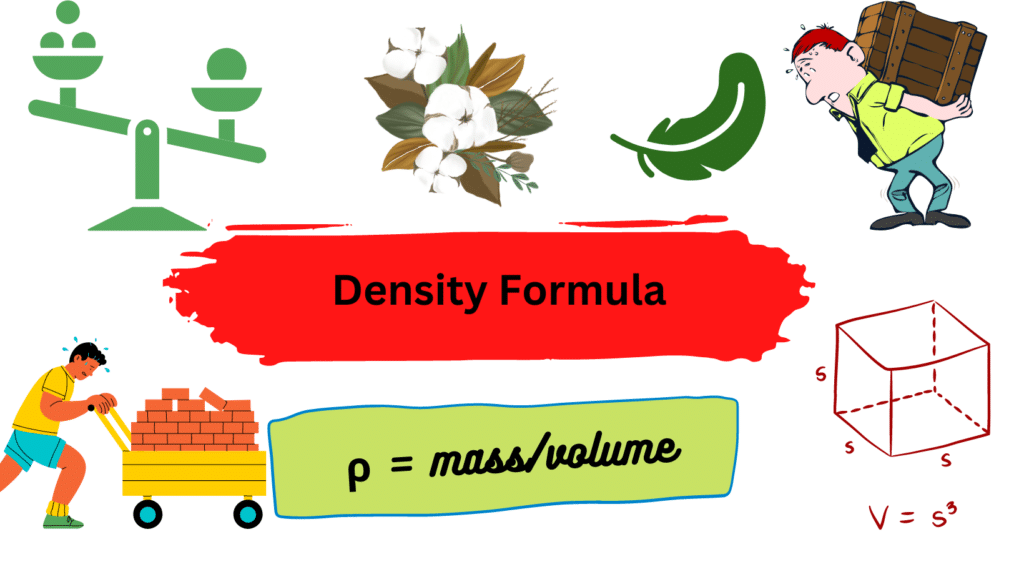
Table of Contents
Density Formula
The density formula is given as:
ρ = m/v
- ρ =density [g/cm3]
- m =mass [g]
- v =volume [cm3]
Density Examples
- Ice is less dense than liquid water, which is why ice cubes float in water.
- Glycerine and mercury are denser than water, they will sink to the bottom if added to it.
- Due to the presence of a lot of sugar, regular Coke/Pepsi has a higher density than water, so a can of it sinks in water. Diet Coke/Pepsi, on the other hand, has a lower density, so a can of it floats.
- The density of honey is greater than the density of water
- Milk is denser than water due to the presence of protein and fat molecules.
Density Facts
- Density is defined as the amount of mass per unit volume. A dense object is one that is heavy and compact.
- The density of any substance is calculated by dividing the mass by the volume of the substance.
- The density of an object is defined by its composition as well as its temperature; for example, cold air is denser than hot air.
- The density of objects explains why some float while others sink. Objects that are less dense float in a more dense liquid. Oil, for example, floats on water because its density is lower than that of water.
- the density of water is 1 gram per cubic centimetre
- The density of an object is directly proportional to its mass and inversely proportional to its volume.
- Density is typically classified into two types: absolute density and relative density. Relative density, also known as specific gravity, is the ratio of a substance’s density to the density of a given reference material. It is a quantity with no units. Absolute density s the mass of any substance per unit volume of a material. It is usually expressed in grams per cubic centimetre (g/cm3)
Difference between density and mass
| Mass | Density | |
| Definition | Amount of matter contained in an object | In material, density refers to the closeness of the atoms, or how densely atoms are packed. |
| Property | Extrinsic | Intrinsic |
| SI unit | Kg | Kg/m3 |
| Formula | mass=density×volume | Density = mass/volume |
More Links
Latest posts by Umair Javaid, PhD Student (see all)
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023



