Einstein’s mass-energy equivalence formula (E = mc²), also known as the mass-energy equivalence, is one of his most famous contributions. It is a well-known equation in physics and mathematics that shows what happens when mass is converted to energy or energy is converted to mass.
Einstein’s equation is expressed quantitatively as:
E = mc2
- E = energy equivalent to the mass (assuming that it is at rest) (J)
- m = mass (kg)
- c = speed of light (m.s-1)
According to Einstein’s equation, energy and mass (matter) are interchangeable; they are different manifestations of the same thing. Energy can become mass and vice versa under the right conditions.
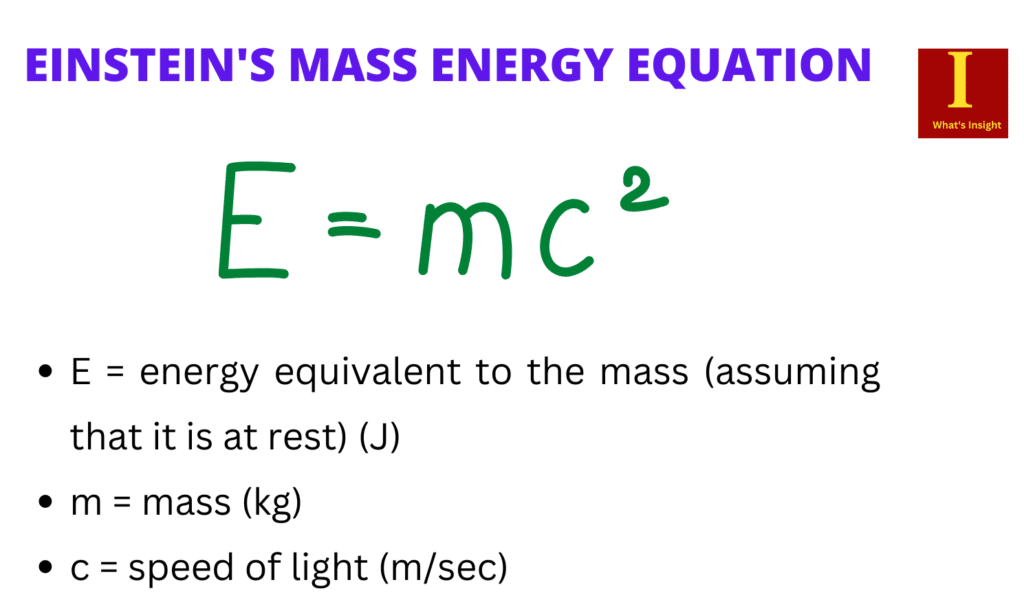
Significance of Einstein’s Mass Energy Formula
One of the most significant functions of the mass-energy equivalence formula is understanding nuclear energy and reactions. For instance, heavy atoms, for example, split into smaller particles and elements during the fission process. Nuclear decay is a process that releases energy from the atom itself.
Real Life Examples of Einstein’s Mass Equation
| No. | Real-Life Examples | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nuclear Power | Nuclear power plants generate electricity by converting a small amount of mass into a large amount of energy through nuclear reactions. The mass-energy equivalence equation helps engineers design more efficient nuclear power plants. |
| 2 | Nuclear Weapons | The development of nuclear weapons is based on the principle that a small amount of mass can be converted into a large amount of energy, as explained by Einstein’s equation. |
| 3 | Medical Imaging | Medical imaging technologies such as PET and SPECT use radioactive materials to create images of the body’s internal organs and tissues. The mass-energy equivalence equation is used to calculate the amount of energy that is released during these imaging procedures. |
| 4 | Particle Accelerators | Particle accelerators use Einstein’s equation to accelerate subatomic particles to high speeds by increasing their energy, which is calculated using the mass-energy equivalence equation. |
| 5 | Sun’s Energy | The sun’s energy is generated by nuclear reactions that convert a small amount of mass into a large amount of energy, as predicted by Einstein’s equation. |
| 6 | Mass Defect in Atomic Nuclei | When atomic nuclei are formed, the mass of the nucleus is always less than the sum of the masses of its individual protons and neutrons. This mass deficit is due to the conversion of some of the mass into energy, as predicted by Einstein’s equation. |
Exams Related Questions
| 1 | What is Einstein’s mass-energy equation? | Einstein’s mass-energy equation is E=mc^2, where E is energy, m is mass, and c is the speed of light. |
| 2 | State the equation for the mass-energy equivalence proposed by Einstein. | The equation for the mass-energy equivalence proposed by Einstein is E=mc^2. |
| 3 | How did Einstein arrive at the mass-energy equivalence equation? | Einstein arrived at the mass-energy equivalence equation by combining the principles of special relativity and classical mechanics. He realized that energy and mass are equivalent, and that mass can be converted into energy, and vice versa. |
| 4 | According to the mass-energy equivalence equation, what is the relationship between mass and energy? | According to the mass-energy equivalence equation, there is a direct relationship between mass and energy, where energy is equal to mass multiplied by the speed of light squared. This means that a small amount of mass can be converted into a large amount of energy, and vice versa. |
| 5 | How is the mass-energy equivalence equation related to the concept of nuclear energy? | The mass-energy equivalence equation is related to the concept of nuclear energy because it explains how nuclear reactions release a tremendous amount of energy by converting a small amount of mass into energy. This is the principle behind nuclear power plants and nuclear weapons. |
| 6 | What is the significance of the mass-energy equivalence equation in the development of nuclear technology? | The mass-energy equivalence equation is significant in the development of nuclear technology because it explains how a small amount of mass can be converted into a large amount of energy, which is the principle behind nuclear reactions. This understanding has led to the development of nuclear power plants and nuclear weapons, which have both positive and negative impacts on society. |
More Links
| Efficiency Formula in Terms of Energy | Energy Density| Definition, and Formula |
| Planck’s Constant – Definition, Formula, and Applications | Nuclear Binding Energy Formula| Step By Step Calculation |
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023